Online first
Current issue
Archive
Most cited in 2024
About the Journal
Editorial Office
Editorial Board
Copyright and self-archiving policy
Information clause on the processing of personal data
Declaration of accessibility
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Reviewers
Contact
Reviewers
2024
2023
2022
2020
2021
2019
2018
2017
2016
2015
2014
2013
Editing and translations
PRELIMINARY REPORT
Artificial Intelligence and employee's health – new challenges
1
Instytut Medycyny Pracy im. prof. J. Nofera / Nofer Institute of Occupational Medicine, Łódź, Poland (Klinika Chorób Zawodowych i Zdrowia Środowiskowego / Clinic of Occupational Diseases and Environmental Health)
Online publication date: 2023-08-28
Corresponding author
Jolanta Walusiak-Skorupa
Instytut Medycyny Pracy im. prof. J. Nofera, Klinika Chorób Zawodowych i Zdrowia Środowiskowego, ul. św. Teresy 8, 91-348 Łódź
Instytut Medycyny Pracy im. prof. J. Nofera, Klinika Chorób Zawodowych i Zdrowia Środowiskowego, ul. św. Teresy 8, 91-348 Łódź
Med Pr Work Health Saf. 2023;74(3):227-33
KEYWORDS
health careoccupational health servicesartificial intelligencetechnological revolutionlearning systemsworker’s health and safety
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
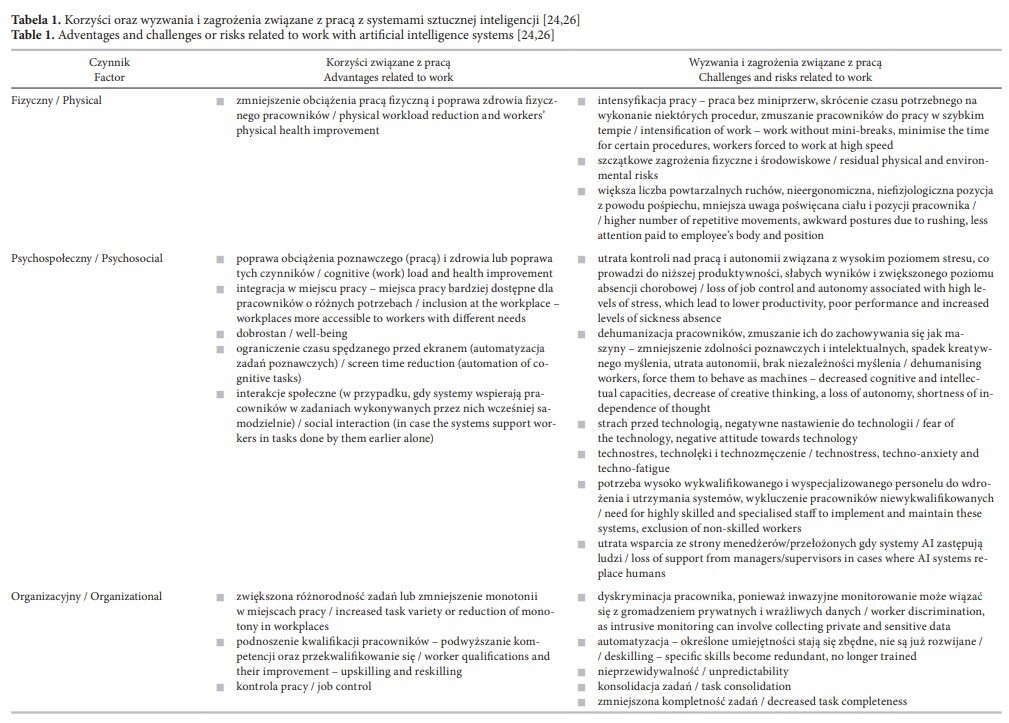
Background: The presence of artificial intelligence (AI) in many areas of social life is becoming widespread. The advantages of AI are being observed in medicine, commerce, automobiles, customer service, agriculture and production in factory settings, among others. Workers first encountered robots in the work environment in the 1960s. Since then, intelligent systems have become much more advanced. The expansion of AI functionality in the work environment exacerbates human health risks. These can be physical (lack of adequate machine control, accidents) or psychological (technostress, fear, automation leading to job exclusion, changes in the labour market, widening social differences). Material and Methods: The purpose of this article is to identify, based on selected literature, possible applications of AI and the potential benefits and risks for humans. Results: The main area of interest was the contemporary work environment and the health consequences associated with access to smart technologies. A key research area for us was the relationship between AI and increased worker control. Conclusions: In the article, the authors emphasize the importance of relevant EU legislation that guarantees respect for the rights of the employed. The authors put forward the thesis that the new reality with the widespread use of AI, requires an analysis of its impact on the human psycho-social and health situation. Thus, a legal framework defining the scope of monitoring and collection of sensitive data is necessary. Med Pr. 2023;74(3):227–33
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.