Online first
Current issue
Archive
Most cited in 2024
About the Journal
Editorial Office
Editorial Board
Copyright and self-archiving policy
Information clause on the processing of personal data
Declaration of accessibility
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Reviewers
Contact
Reviewers
2024
2023
2022
2020
2021
2019
2018
2017
2016
2015
2014
2013
Editing and translations
REVIEW PAPER
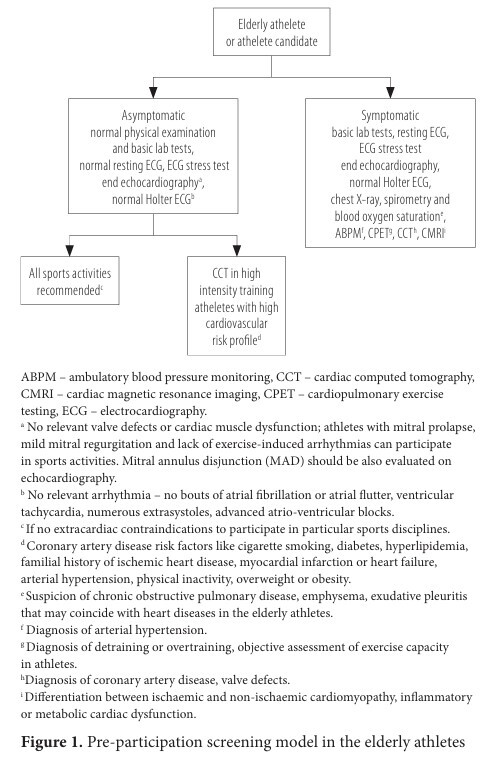
Cardiovascular screening of elderly athletes
1
Medical Centre PZU Health, Wrocław, Poland
2
Wrocław University of Science and Technology, Wrocław, Poland
(Faculty of Medicine)
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Online publication date: 2024-04-04
Corresponding author
Anna Janocha
Wrocław University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Medicine, Hoene-Wrońskiego 13c, 58-376 Wrocław
Wrocław University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Medicine, Hoene-Wrońskiego 13c, 58-376 Wrocław
Med Pr Work Health Saf. 2024;75(3):233-41
KEYWORDS
cardiovascular diseasesphysical activitysudden cardiac deathcardiovascular complicationselderly athletescardiovascular screening
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
The permanently growing interest in amateur and professional sports activities among young, middle-aged and elderly athletes raises serious concerns about athletes’ health, the safety of physical training, and the sports-related risk of sudden cardiac death and other cardiovascular complications during exercise. In recent years there has been an increasing number of cases of sudden cardiac death during physical effort. At present, life expectancy in the most developed countries grows rapidly and the number of people >65 years dramatically increases. Moreover, biological age of the population is lower. Subsequently, relevant increase in the number of elderly athletes involved in various types of sports activities has been reported in many countries. It was also demonstrated that physical activity has strong beneficial effect on cognitive functions, psychomotor performance and thus exercise capacity, which is very important for the elderly people in their everyday routine activities. Nonetheless, it should be remembered that participation in amateur and professional sports activities may be associated with risk of serious cardiovascular events in the elderly athletes often suffering from various civilization diseases. It is also reported that the number of elderly people after interventional cardiology procedures, open heart surgery and cancer treatment (chemotherapy, radiotherapy), who wish to participate in various sports activities, systematically grows. The authors of the paper conduct a literature review on cardiovascular risk assessment in the elderly athletes including the contemporary cardiology diagnostic methods and diagnostic schemes to prevent sudden cardiac death and other cardiovascular events during exercise. The controversies over efficacy of particular diagnostic tools to detect cardiovascular diseases in the elderly athletes and worldwide epidemiologic data concerning risk of sudden cardiac death during physical exercise have been also presented. Here, the authors have derived suggestions for establishment of comprehensive diagnostic schemes to prevent sudden cardiac death during sports activities. Med Pr Work Health Saf. 2024;75(3):233–241
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.