Online first
Current issue
Archive
Most cited in 2024
About the Journal
Editorial Office
Editorial Board
Copyright and self-archiving policy
Information clause on the processing of personal data
Declaration of accessibility
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Reviewers
Contact
Reviewers
2024
2023
2022
2020
2021
2019
2018
2017
2016
2015
2014
2013
Editing and translations
REVIEW PAPER
Androgen receptor modulation and bladder cancer prevention – a short review
1
Nofer Institute of Occupational Medicine, Łódź, Poland (Department of Translational Research)
2
Institute of Biomedical and Genetic Engineering (IBGE), Islamabad, Pakistan (Department of Molecular Oncology)
Online publication date: 2022-03-14
Corresponding author
Edyta Wieczorek
Nofer Institute of Occupational Medicine, Department of Translational Research, św. Teresy 8, 91-348 Łódź, Poland
Nofer Institute of Occupational Medicine, Department of Translational Research, św. Teresy 8, 91-348 Łódź, Poland
Med Pr Work Health Saf. 2022;73(2):151-62
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
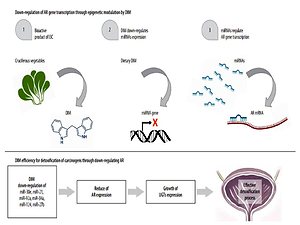
The prevalence of bladder cancer (BCa) is 4 times higher in men as compared to women, and gender differences have been the focus of attention for few years. Androgen receptor (AR) may be a putative explanation for gender differences. It may also be related to unfavourable BCa progression and development because of the increased androgen sensitivity of urothelium to carcinogens. Moreover, cigarette smoking and occupational exposure to carcinogens have been reported to play contributory roles with the highest attributable risk of BCa. In this review, the authors attempt to summarize the seminal research works that synthesized current understanding of the central role of AR in the negative regulation of carcinogen detoxification activity in BCa. In particular, the authors discuss the regulatory effects of 3,3’-diindolylmethane on AR gene transcription through microRNA as its suggested effect on the prevention of BCa. Moreover, to show the still existing problem of occupational exposure and BCa incidence, the authors review recent studies in this area. Based on the rapidly accumulating scientific evidence, it seems pragmatic that androgen/AR-mediated interference in the detoxification mechanism may be inhibited by phytochemicals. Therefore, collectively, nutrition has a key role as gene–nutrient interactions are important contributors to BCa prevention, also through epigenetic modifications. Here, the authors have derived suggestions for future research. Med Pr. 2022;73(2):151–62
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.